- 翰林提供學(xué)術(shù)活動、國際課程、科研項目一站式留學(xué)背景提升服務(wù)!
- 400 888 0080
EDEXCEL IGCSE CHEMISTRY: DOUBLE SCIENCE 復(fù)習(xí)筆記:4.2.4 Cracking
EDEXCEL IGCSE CHEMISTRY: DOUBLE SCIENCE 復(fù)習(xí)筆記:4.2.4 Cracking
Cracking
- Saturated molecules contain?single?bonds only whereas unsaturated molecules contain?double?bonds between their carbon atoms
- Alkanes?are saturated compounds and?alkenes?are unsaturated compounds
- Long chain alkane molecules are further processed to produce other products consisting of smaller chain molecules
- A process called?cracking?is used to convert them into short chain molecules which are more useful
- Small alkenes?and?hydrogen?are produced using this process
- Kerosene and diesel oil are often cracked to produce petrol, other alkenes and hydrogen
- There are two methods used to crack alkanes:?catalytic?cracking and?steam?cracking
- As the names suggest, one method uses a catalyst and the other uses steam
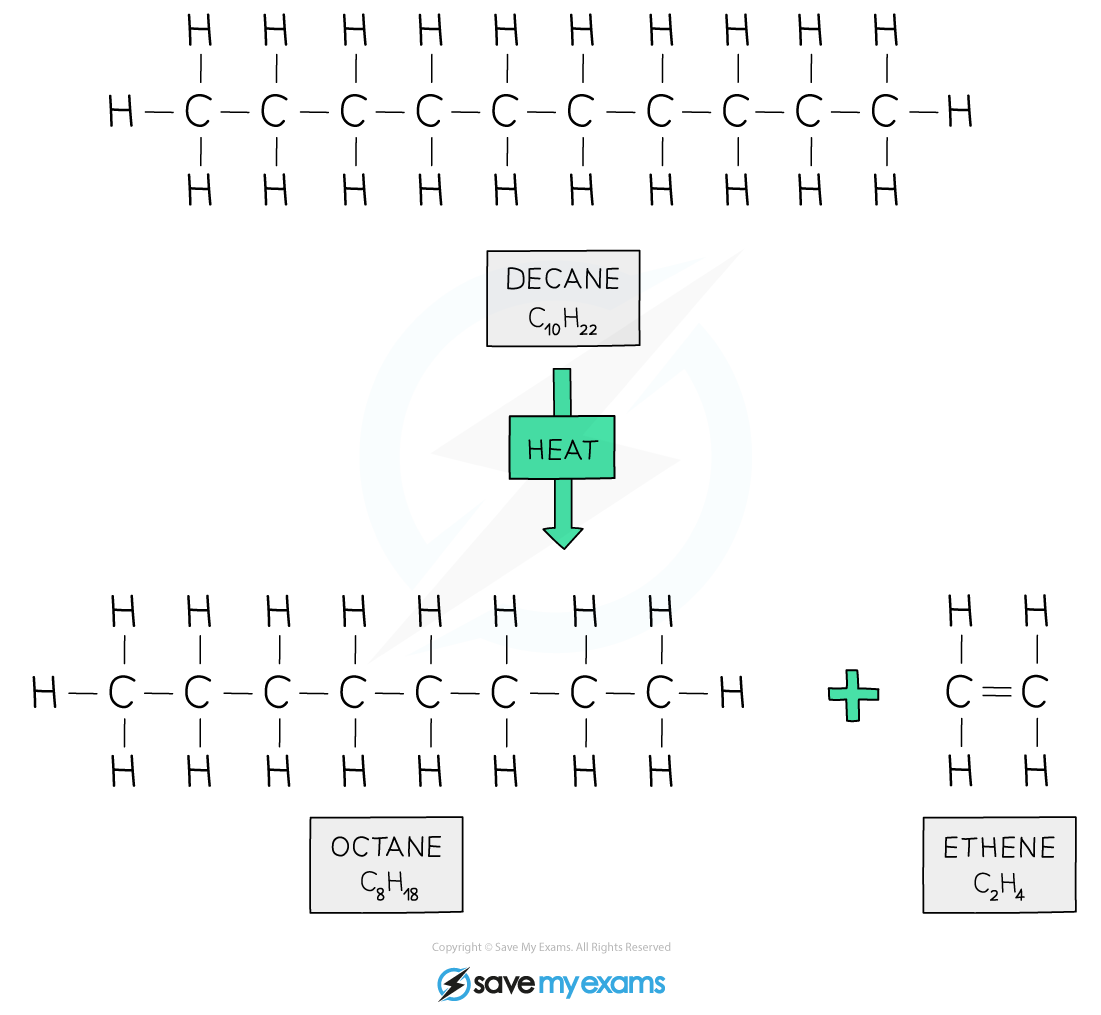
Decane is cracked to produce octane for petrol and ethene for ethanol synthesis
- Catalytic cracking?involves heating the hydrocarbon molecules to around 470 – 550°C to?vaporise?them
- The vapours then pass over a hot powdered?catalyst?of aluminium oxide
- This process breaks covalent bonds in the molecules as they come into contact with the surface of the catalyst, causing?thermal decomposition?reactions
- The molecules are broken up in a random way which produces a mixture of smaller alkanes and alkenes
- Hydrogen and a higher proportion of alkenes are formed at higher temperatures and higher pressure
Fraction Supply & Demand
- Crude oils vary considerably in their composition and some need more refining than others
- Supply?is how much of a particular fraction can be produced from refining the crude oil
- Demand?is how much customers want to buy
- General the demand for certain fractions outstrips the supply so this is why?cracking?is necessary to convert surplus unwanted fractions into more useful ones
- This is mostly larger, heavier fractions that are cracked into smaller lighter fractions
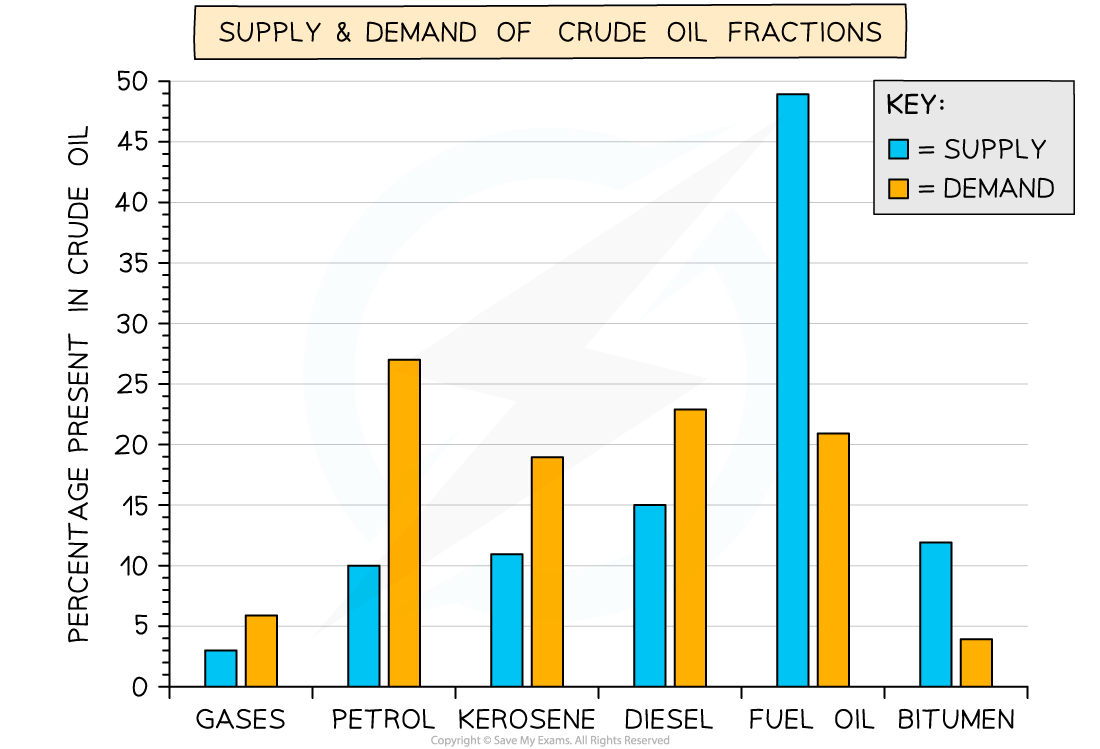
Supply & demand graph for crude oil fractions
- You can see from the chart that fuel oil and bitumen are surplus fractions so they are cracked and modified to produce petrol, kerosene and diesel
Exam Tip
Remember that cracking is an?endothermic?reaction.
轉(zhuǎn)載自savemyexams

最新發(fā)布
? 2025. All Rights Reserved. 滬ICP備2023009024號-1









