- 翰林提供學術活動、國際課程、科研項目一站式留學背景提升服務!
- 400 888 0080
AQA A Level Chemistry復習筆記5.1.6 Entropy
Entropy
- You may have wondered why it is that?endothermic?reactions occur at all, after all, what can be the driving force behind endothermic reactions if the products end up in a less stable, higher energy state?
- Although the majority of chemical reactions we experience everyday are?exothermic,? ΔH??alone is not enough to explain why endothermic reactions occur
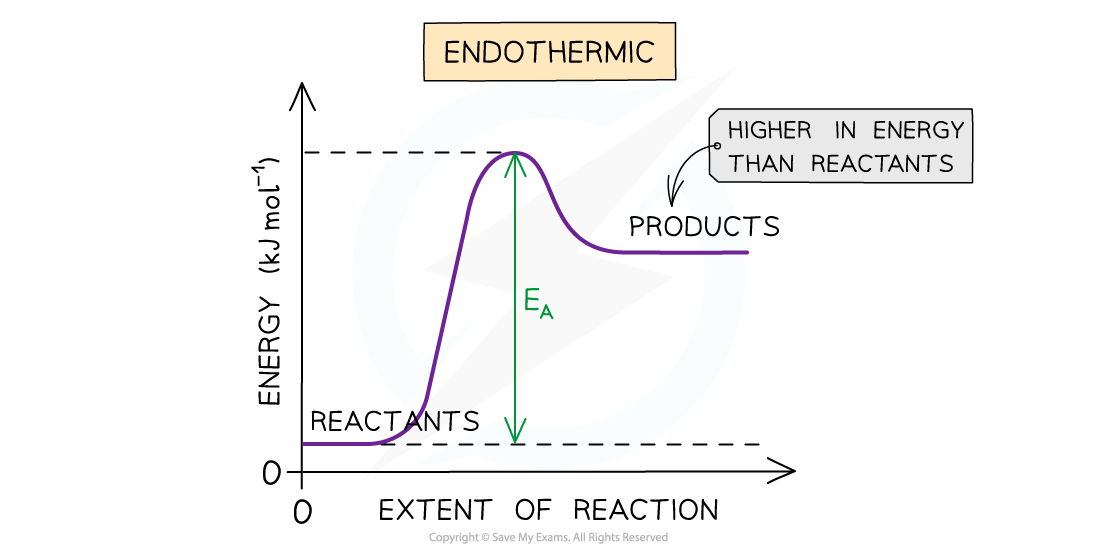
The driving force behind chemical reactions cannot be explained by enthalpy changes alone as it makes not sense for chemical to end up in a less stable higher energy state in endothermic reactions
- The answer is?entropy
Chaos in the universe
- The?entropy (S)?of a given system is the number of possible arrangements of the particles and their energy in a given system
- In other words, it is a measure of how?disordered?or?chaotic?a system is
- When a system becomes?more disordered, its entropy will?increase
- An increase in entropy means that the system becomes?energetically more stable
- For example, during the thermal decomposition of calcium carbonate (CaCO3) the entropy of the system increases:
CaCO3(s) → CaO(s) + CO2(g)
- In this decomposition reaction, a gas molecule (CO2) is formed
- The CO2?gas molecule is more disordered than the solid reactant (CaCO3), as it is constantly moving around
- As a result, the system has become more?disordered?and there is an?increase?in?entropy
- Another typical example of a system that becomes more disordered is when a solid is?melted
- For example, melting ice to form liquid water:
H2O(s) → H2O(l)
- The water molecules in ice are in fixed positions and can only vibrate about those positions
- In the liquid state, the particles are still quite close together but are arranged more randomly, in that they can move around each other
- Water molecules in the liquid state are therefore more?disordered
- Thus, for a given substance, the?entropy?increases?when its solid form melts into a liquid
- In both examples, the system with the?higher?entropy?will be?energetically favourable?(as the energy of the system is more spread out when it is in a disordered state)
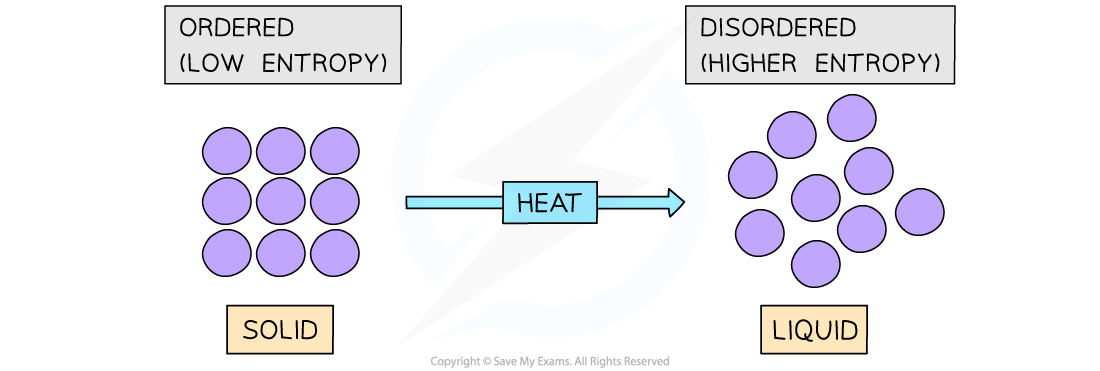
Melting a solid will cause the particles to become more disordered resulting in a higher entropy state
Feasible or spontaneous reactions
- Chemists talk about reactions being?feasible?or?spontaneous
- What they mean is that reactions take place of their own accord, in other words, they are energetically favourable
- This is an outcome of the?second law of thermodynamics?which broadly states the the entropy of the universe is always increasing
- We can see examples of this all around us:
- cups fall off tables and spontaneously break into many pieces, never the other way around
- hot objects always cool and spread their heat into the surroundings, never the other way around
- Earthquakes destroy buildings and create chaos and disorder
- When living things die they decompose and change from complex ordered systems into disordered simple molecules
- However,?feasibility?takes no account of the?rate of reaction?and states only what is possible, not what actually happens. A feasible reaction might be incredibly slow, such as the rusting of iron.
Exam Tip
Make sure you don’t confuse the system with your surroundings!The system consists of the molecules that are reacting in a chemical reaction.The surroundings are everything else such as the solvent, the air around the reaction, test-tube, etc.
Calculating Entropy Changes
- Entropy changes are an order of magnitude smaller than enthalpy changes, so entropy is measured in joules rather than kilojoules. The full unit for entropy is?J K-1?mol-1
- The standard entropy change (ΔSsystem??) for a given reaction can be calculated using the standard entropies (S??) of the reactants and products
- The equation to calculate the standard entropy change of a system is:
ΔSsystem??= ΣΔSproducts??- ΣΔSreactants?
(where Σ = sum of)
- For example, the standard entropy change for the formation of ammonia (NH3) from nitrogen (N2) and hydrogen (H2) can be calculated using this equation
N2(g) + 3H2(g) ? 2NH3(g)
ΔSsystem??= (2 x ΔS?(NH3)) - (ΔS?(N2) + 3 x ΔS?(H2))
- Notice that, unlike enthalpy of formation for elements, entropy for elements is?not?zero and you can find entropy values for elements and compounds in data books
Worked Example
Calculating entropy changesCalculate the entropy change of the system for the following reaction:
2Mg (s) + O2?(g) → 2MgO (s)
S?[Mg(s)] = 32.60 J K-1?mol-1
S?[O2(g)] = 205.0 J K-1?mol-1
S?[MgO(s)] = 38.20 J K-1?mol-1
Answer
ΔSsystem??= ΣΔSproducts??- ΣΔSreactants?
ΔSsystem??= (2 x 38.20) - (2 x 32.60 + 205.0)
=?-193.8 J K-1?mol-1
Exam Tip
Use the?stoichiometry? of the equation and the correct state of the compounds when calculating the entropy change of a reaction.
轉載自savemyexams

最新發布
? 2025. All Rights Reserved. 滬ICP備2023009024號-1









