- 翰林提供學(xué)術(shù)活動(dòng)、國(guó)際課程、科研項(xiàng)目一站式留學(xué)背景提升服務(wù)!
- 400 888 0080
AQA A Level Biology復(fù)習(xí)筆記1.3.3 Protein Structure & Function
Proteins: Structures & Functions
- There are?four?levels of structure in proteins, three are related to a single polypeptide chain and the fourth level relates to a protein that has two or more polypeptide chains
- Polypeptide or protein molecules can have anywhere from 3 amino acids (Glutathione) to more than 34,000 amino acids (Titan) bonded together in chains
Primary
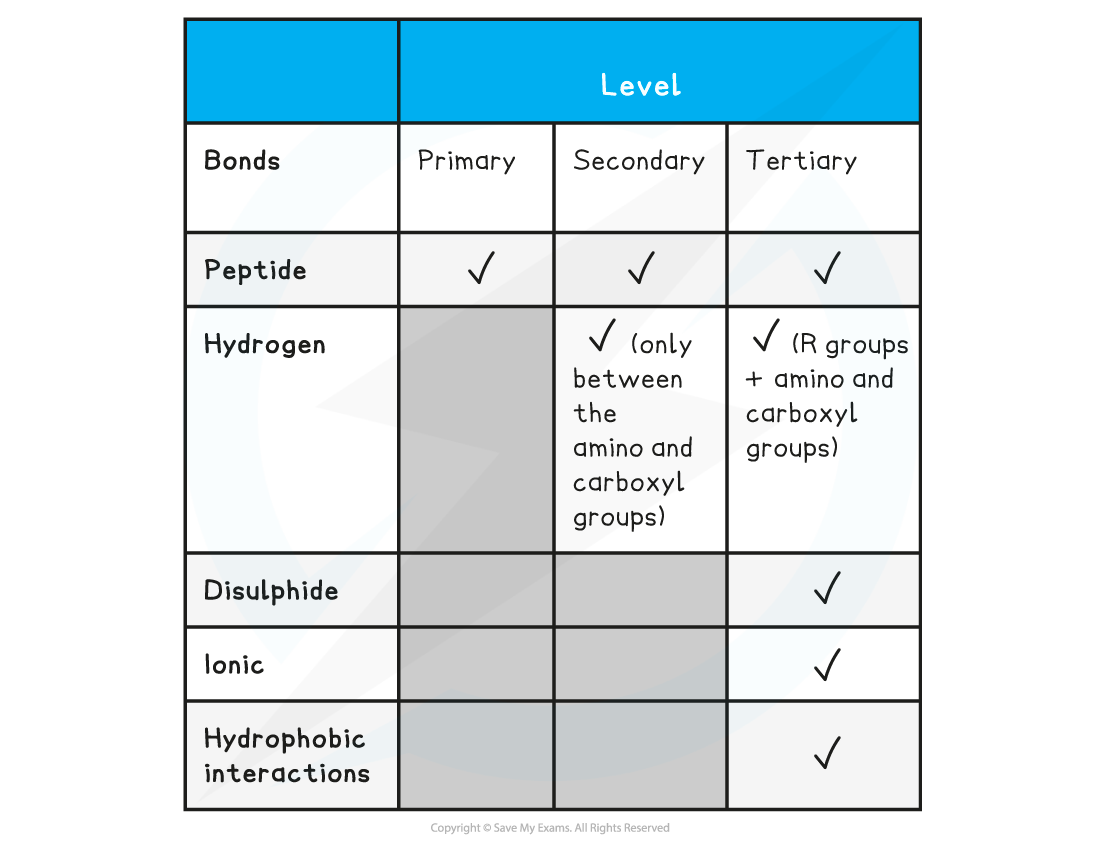
- The sequence of amino acids bonded by covalent peptide bonds is the?primary structure?of a protein
- DNA?of a cell?determines?the primary structure of a protein by instructing the cell to add certain amino acids in specific quantities in a certain sequence. This affects the shape and therefore the function of the protein
- The primary structure is?specific?for each protein (one alteration in the sequence of amino acids can affect the function of the protein)
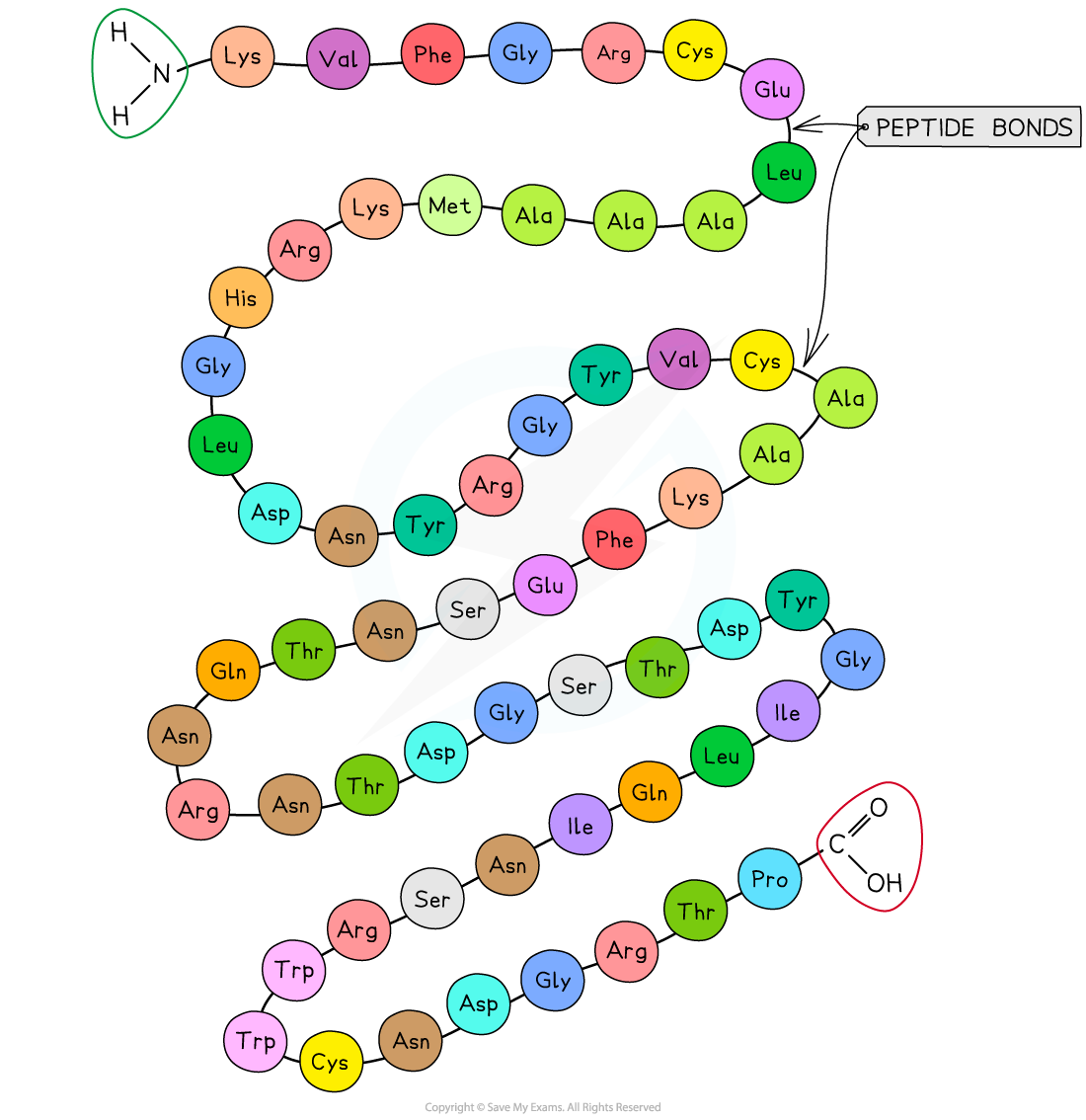
The primary structure of a protein. The three-letter abbreviations indicate the specific amino acid (there are 20 commonly found in cells of living organisms)
Secondary
- The?secondary structure?of a protein occurs when the weak negatively charged nitrogen and oxygen atoms interact with the weak positively charged hydrogen atoms to form?hydrogen bonds
- There are two shapes that can form within proteins due to the hydrogen bonds:
- α-helix
- β-pleated sheet
- The?α-helix?shape occurs when the hydrogen bonds form between every?fourth?peptide bond (between the oxygen of the carboxyl group and the hydrogen of the amine group)
- The?β-pleated sheet?shape forms when the protein folds so that?two parts of the polypeptide chain?are?parallel?to each other enabling hydrogen bonds to form between parallel peptide bonds
- Most?fibrous?proteins have secondary structures (e.g. collagen and keratin)
- The?secondary structure?only?relates to?hydrogen bonds?forming between the?amino group?and the?carboxyl group?(the ‘protein backbone’)
- The hydrogen bonds can be broken by high temperatures and pH changes
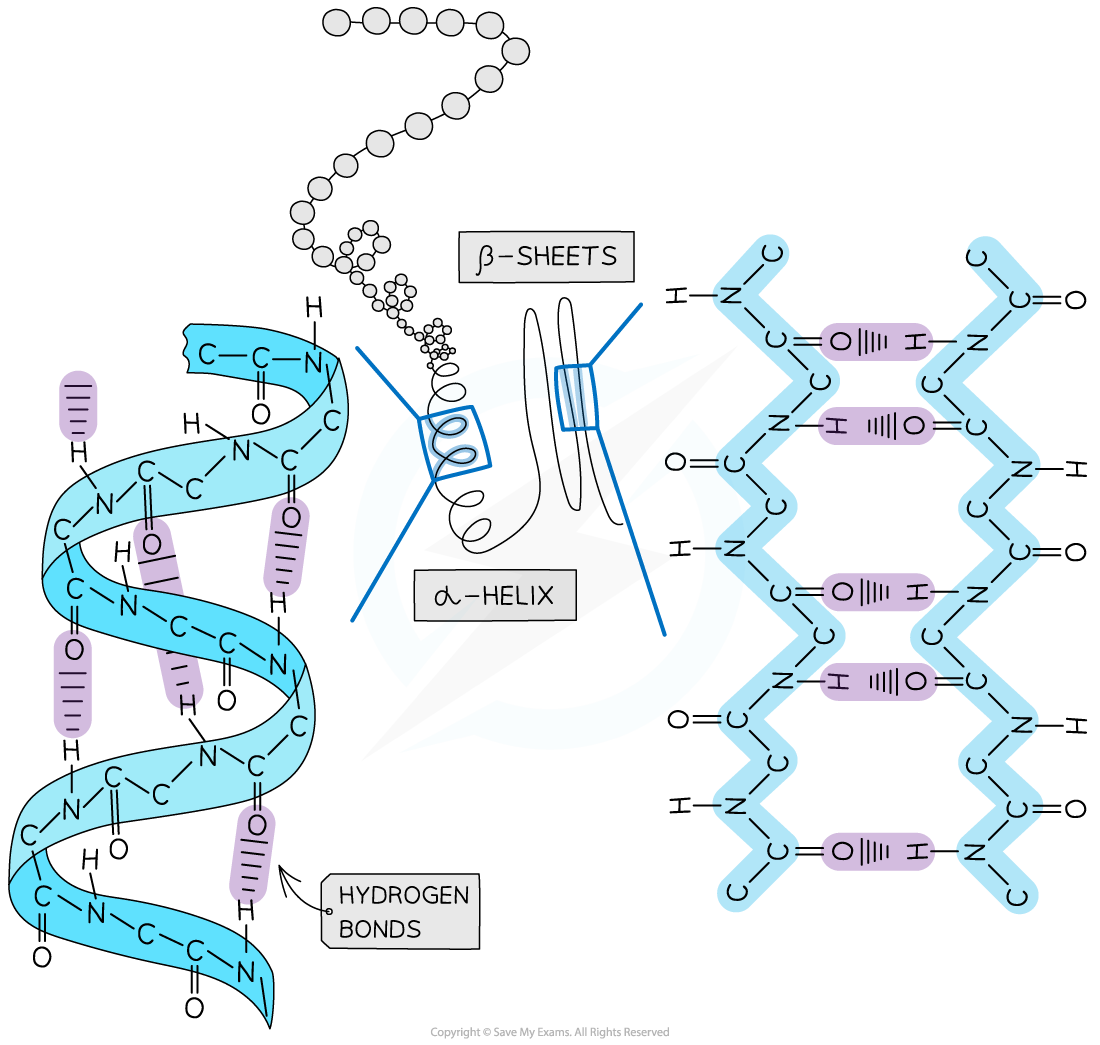
The secondary structure of a protein with the α-helix and β-pleated sheet shapes highlighted. The magnified regions illustrate how the hydrogen bonds form between the peptide bonds
Tertiary
- Further conformational change of the secondary structure leads to additional bonds forming between the?R groups?(side chains)
- The additional bonds are:
- Hydrogen?(these are between R groups)
- Disulphide?(only occurs between cysteine amino acids)
- Ionic?(occurs between charged R groups)
- Weak?hydrophobic interactions?(between non-polar R groups)
- This structure is common in?globular?proteins
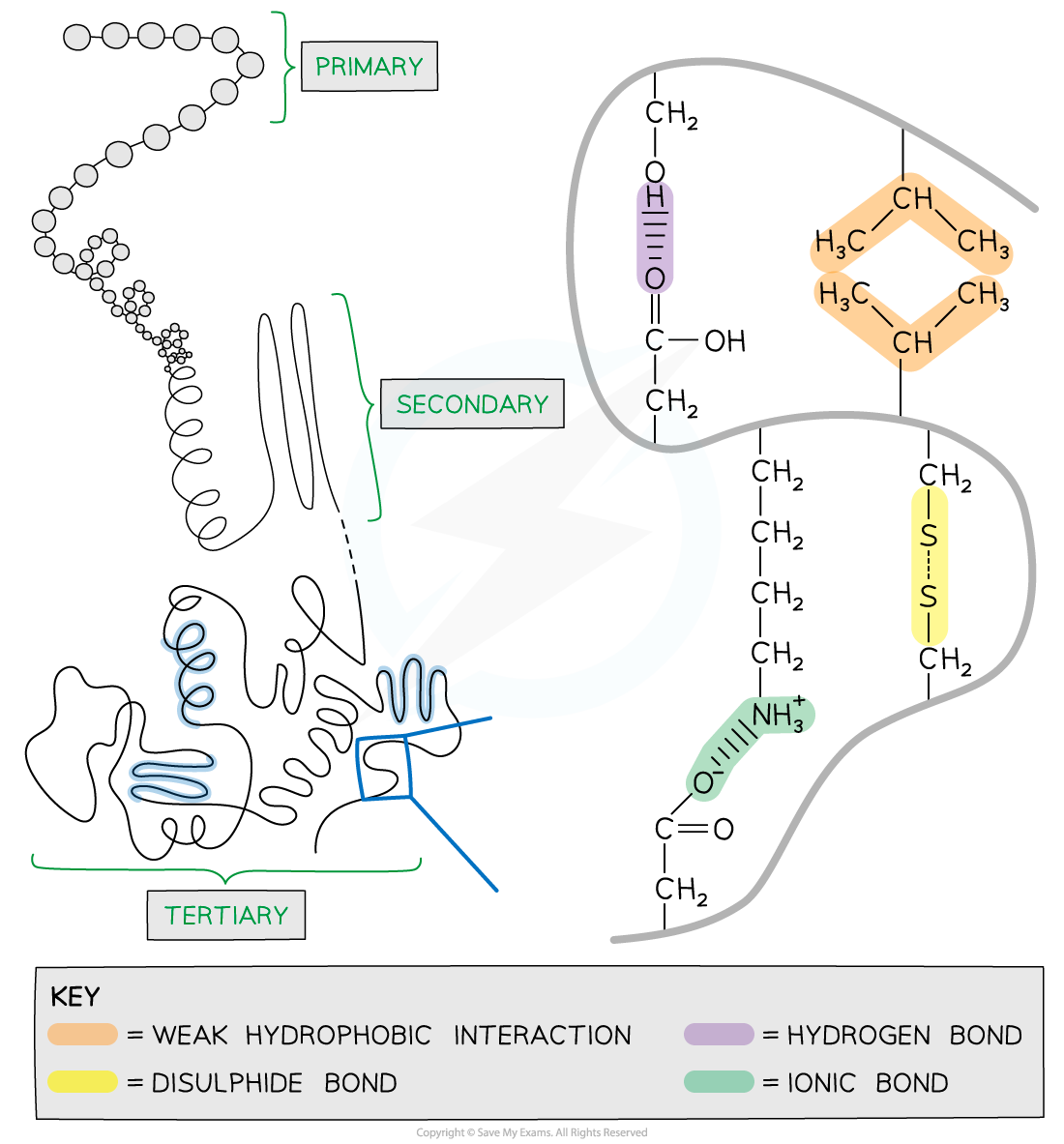
The tertiary structure of a protein with hydrogen bonds, ionic bonds, disulphide bonds and hydrophobic interactions formed between the R groups of the amino acids
Quaternary
- Occurs in proteins that have?more than one?polypeptide chain working together as a functional macromolecule, for example, haemoglobin
- Each polypeptide chain in the quaternary structure is referred to as a?subunit?of the protein
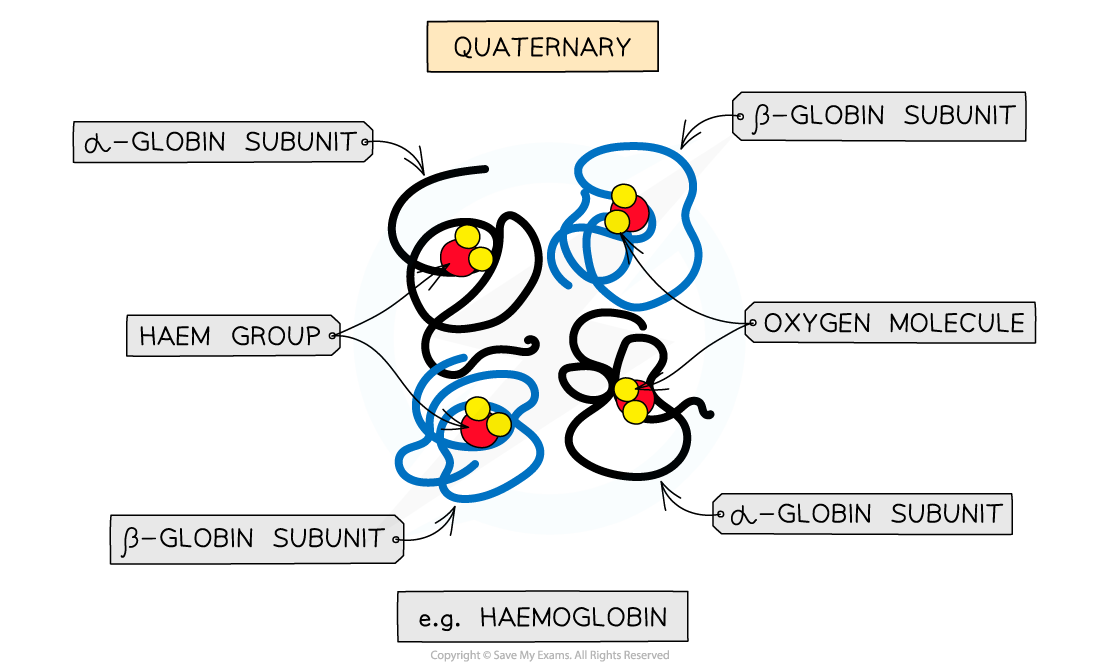
The quaternary structure of a protein. This is an example of haemoglobin which contains four subunits (polypeptide chains) working together to carry oxygen
Summary of Bonds in Proteins Table
轉(zhuǎn)載自savemyexams

最新發(fā)布
? 2025. All Rights Reserved. 滬ICP備2023009024號(hào)-1









