- 翰林提供學術活動、國際課程、科研項目一站式留學背景提升服務!
- 400 888 0080
CIE A Level Chemistry復習筆記7.4.3 Reactions of Phenol
Reactions of Phenol
- Phenols can undergo many types of reactions as both the?electron-rich benzene ring?and the?polar -OH?group can participate in chemical reactions
- Some of the reactions of phenols include:
- With bases
- With reactive metals
- With diazonium salts
- Nitration
- Bromination
Reactions of the -OH group in phenols
- The -OH group in phenols has a?slightly acidic character
- It can therefore act as an?acid?and take part in?acid-base reactions
Reaction with bases
- Phenols are?only slightly soluble?in water due to the large non-polar benzene ring
- However, they do dissolve in alkaline solutions and undergo?acid-base?reactions with?bases?to form a?soluble salt?and?water

Phenols are weak acids and undergo acid-base reactions in alkaline solutions
Reaction with reactive metals
- Molten phenols?react?vigorously?with reactive metals such as?sodium?(Na)
- This is also an?acid-base?reaction
- Now, a soluble salt is formed and?hydrogen gas?is given off

Molten phenols react vigorously with reactive metals to form a soluble salt and hydrogen gas
Reaction with diazonium ions
- Diazonium ions?are very reactive compounds containing an -N2+?group
- When phenols are?dissolved?in sodium hydroxide (NaOH), a solution of?sodium phenoxide?is obtained
- This solution is cooled in?ice?and?cold diazonium ion?is added to the sodium phenoxide
- After the reaction has occurred, a?yellow-orange?solution or precipitate of an?azo compound?is formed
- These are compounds in which?two benzene?rings are linked by a?nitrogen bridge
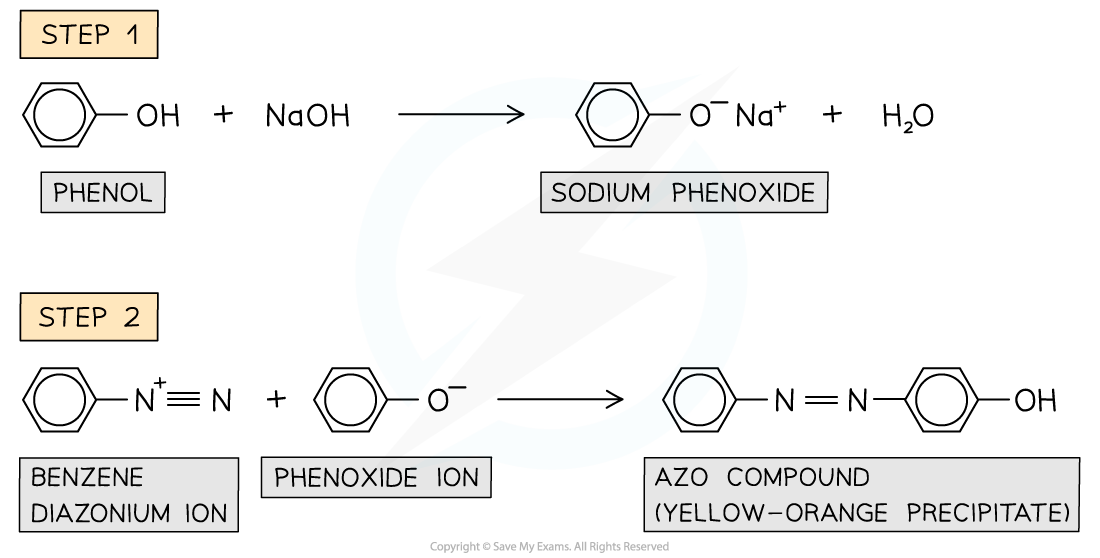
Azo compounds are formed from the reaction of phenols with diazonium ions
Reactions of the aromatic ring in phenols
- Phenols react more?readily?with?electrophiles?compared to benzene
- This is because one of the lone pairs of electrons on the oxygen atom in -OH overlaps with the π bonding system
- This increases the?electron density?of the benzene ring making it more?susceptible?to?electrophilic attack
- The -OH group in phenols is?activating?and?directs?incoming electrophiles to the?2, 4, and 6 positions
Nitration
- Phenols can undergo?electrophilic substitution?reactions when reacted with?dilute nitric acid?(HNO3) at?room temperature?to give a mixture of?2-nitrophenol?and?4-nitrophenol
- When?concentrated HNO3?is used, the product will be 2,4,6-trinitrophenol instead
- A hydrogen atom in the benzene ring is?substituted?by a nitro (-NO2) group
- This is also known as the?nitration?of phenol
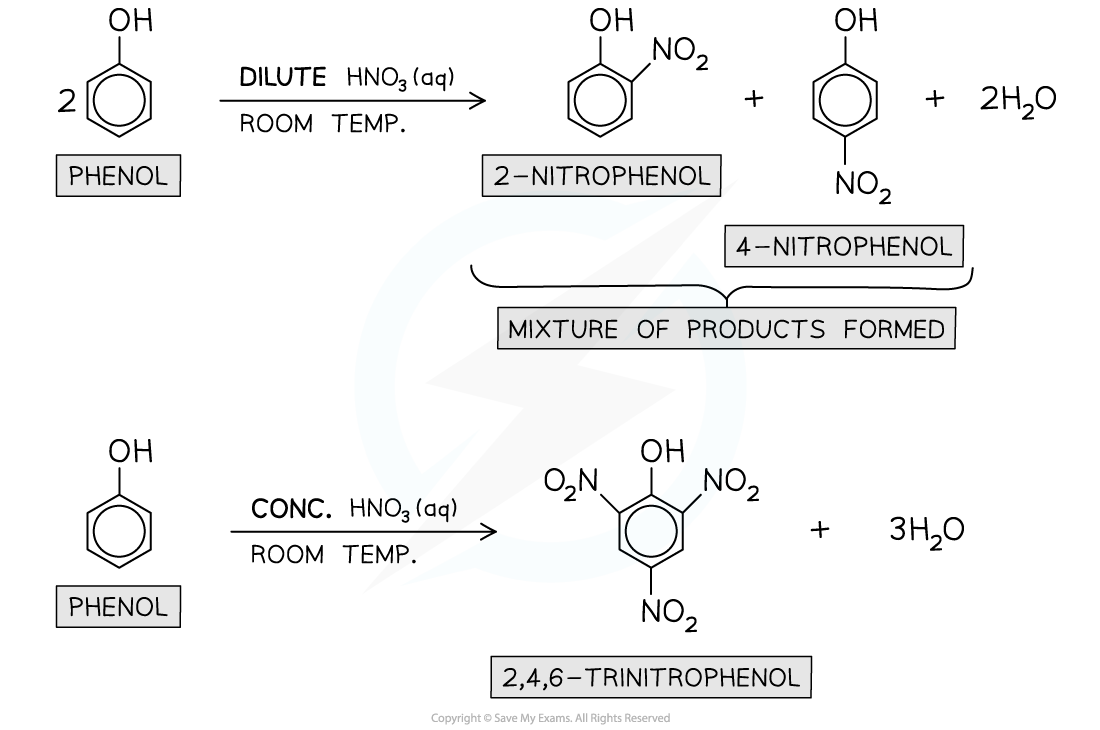
Phenols undergo nitration when reacted with dilute HNO3?at room temperature
Bromination
- Phenols also undergo?electrophilic substitution?reactions when reacted with?bromine water?at?room temperature
- Phenol?decolourises?the?orange?bromine solution to form a?white precipitate?of 2,4,6-tribromophenol
- This is also known as the?bromination?of phenol
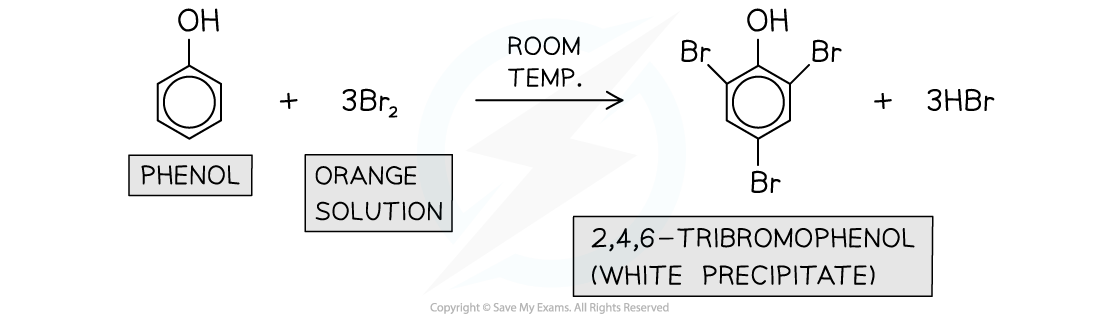
Phenols undergo bromination when reacted with bromine water at room temperature
轉載自savemyexams

最新發布
? 2025. All Rights Reserved. 滬ICP備2023009024號-1









