- 翰林提供學術活動、國際課程、科研項目一站式留學背景提升服務!
- 400 888 0080
IB DP Biology: HL復習筆記2.6.1 Transcription
Transcription
- This process of protein synthesis occurs in?two stages:
- Transcription?–?DNA?is transcribed and an?mRNA?molecule is produced
- mRNA is a single stranded RNA molecule that transfers the information in DNA from the nucleus into the cytoplasm
- mRNA production requires the enzyme RNA polymerase
- Translation?–?mRNA?(messenger RNA) is translated and an?amino acid sequence?is produced
- Transcription?–?DNA?is transcribed and an?mRNA?molecule is produced
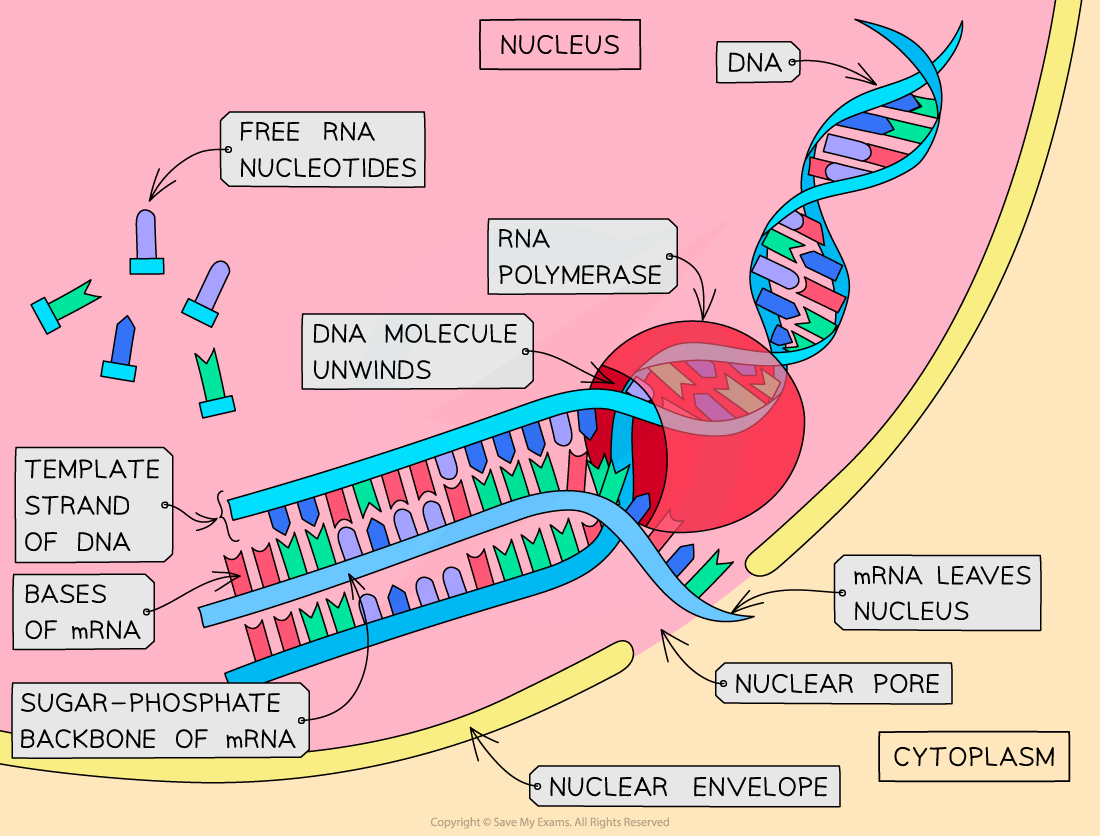
The process of transcription
- This stage of protein synthesis occurs?in the nucleus?of the cell
- Part of a DNA molecule?unwinds?(the?hydrogen bonds?between the complementary base pairs?break)
- This exposes the?gene?to be transcribed (the gene from which a particular polypeptide will be produced)
- A complementary copy of the code from the gene is made by building a?single-stranded nucleic acid molecule known as mRNA?(messenger RNA)
- Free RNA nucleotides?pair up (via hydrogen bonds) with their complementary (now exposed) bases on one strand (the template strand) of the ‘unzipped’ DNA molecule
- The sugar-phosphate groups of these RNA nucleotides are then?bonded?together by the enzyme?RNA polymerase?to form the sugar-phosphate backbone of the mRNA molecule
- When the gene has been transcribed (when the mRNA molecule is complete), the hydrogen bonds between the mRNA and DNA strands break and the?double-stranded DNA molecule re-forms
- The mRNA molecule then?leaves the nucleus?via a pore in the nuclear envelope
- This is where the term?messenger?comes from - the mRNA is despatched,?carrying a message, to another part of the cell
- DNA can't make this journey;?it's too big to fit through the pores in the nuclear envelope
DNA is transcribed and an mRNA molecule is produced
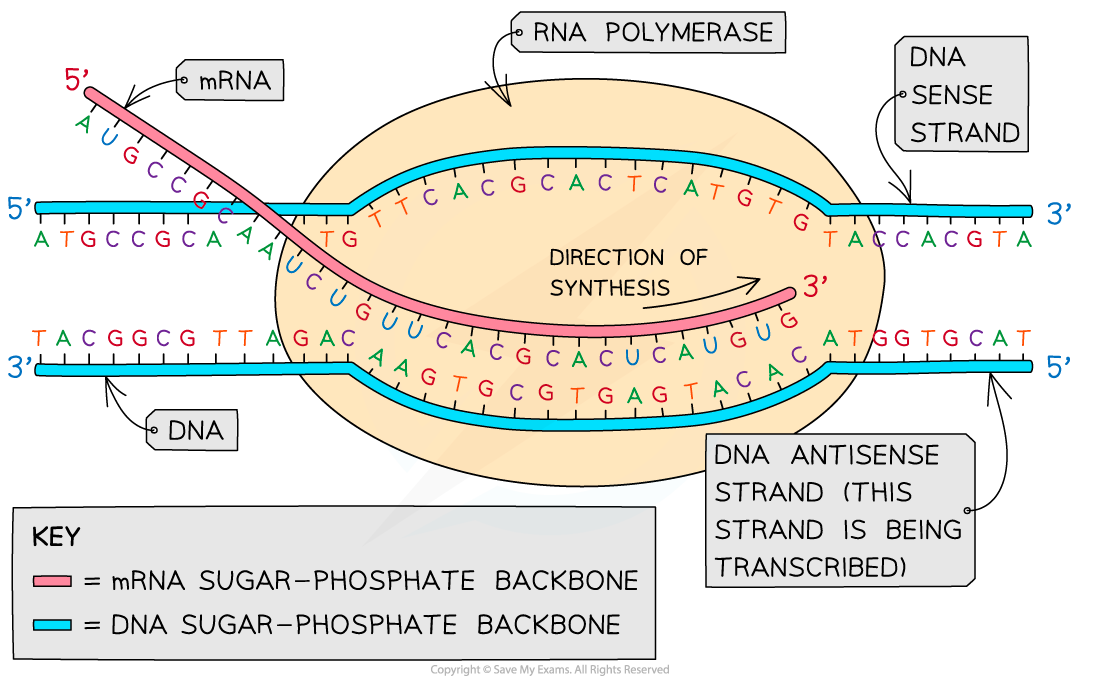
Sense and anti-sense strands
- In the?transcription?stage of protein synthesis, free RNA nucleotides pair up with the exposed bases on the DNA molecule but?only with those bases on one strand of the DNA molecule
- The RNA will have a complementary base sequence to the DNA strand (with the substitution of Thymine with Uracil)
- The strand of the DNA molecule that carries the genetic code is called the?sense strand
- The opposite DNA strand is called the?antisense?strand
- To get?an RNA transcript of the sense strand, the?antisense strand is the one that is transcribed?to form the mRNA molecule
- This mRNA molecule will later be translated into an amino acid chain
The antisense strand of the DNA molecule is the one that is transcribed
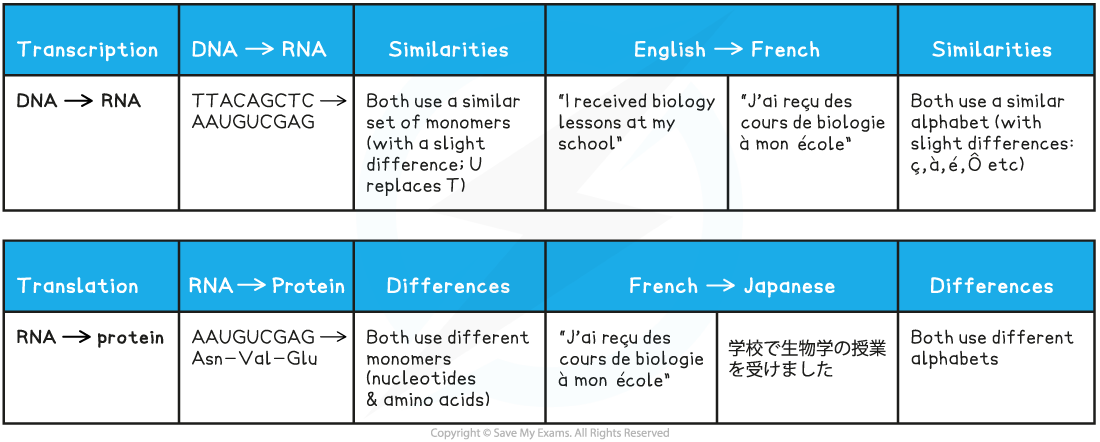
Analogy: Think of transcription and translation as being like converting between languages
- Each language has its?alphabet, just as nucleic acids and proteins have their?monomers
- Transcription?is like converting text from?English?to?French
- The same characters are used, but there are slight differences
- French uses the same alphabet as English but employs occasional accented characters like a, é, or ?
- DNA and RNA employ largely the same monomers, but with the slight difference of U replacing T.
Translation is like converting text from a western language to a language that uses a different alphabet, like?Japanese
- A completely?different set of characters?is used
- The sequence of characters is?unrecognisable?from the original
- If we could see them, a chain of amino acids would look nothing like a chain of nucleotides
Transcription and Translation Can be Likened to Conversion Between Languages Table
Exam Tip
Be careful – DNA polymerase is the enzyme involved in DNA replication; RNA polymerase is the enzyme involved in transcription – don’t get these confused.
轉載自savemyexams

最新發布
? 2025. All Rights Reserved. 滬ICP備2023009024號-1









