- 翰林提供學術活動、國際課程、科研項目一站式留學背景提升服務!
- 400 888 0080
Alevel數學干貨,微積分之鏈式法則
Alevel數學干貨,微積分之鏈式法則
1.The China rule (鏈式法則)
If y=f(u) is a differentiable function of u and u=g(x) is a differentiable function of x, then y=f(g(x)) is a differentiable function of x and
![]()
or, equivalently,
![]()
如果復合函數處處可導,可使用鏈式法則來進行求導,外部函數的導數乘以內部函數的導數。
常考題型解析:
Example 1
![]()
SOLUTION
As you saw earlier, you can break down this expression as follows.
![]()
Differentiation these gives
![]()
and
![]()
By the chain rule
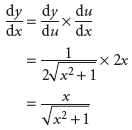
2. Related-Rate Problems
相關變化率問題
Differentiation with respect to different variables
對于不同變量的微分
The chain rule makes it possible to differentiate with respect to a variable which does not feature in the original expression. For example, the volume V of a sphere of radius r is given by
![]()
Differentiating this with respect to r gives the rate of change of volume with radius,
![]()
However you might be more interested in finding dv/dt, the rate of change of change of volume with time, t. To find this, you would use the chain rule:
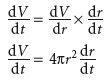
相關變化率問題是復合函數求導的應用,例,半徑為r的球體積為
![]()
體積對半徑進行微分,可得到體積對于半徑的變化率,
![]()
要求出體積對于時間的變化率dV/dt,可以使用鏈式法則,通過半徑r對時間t進行微分。
常考題型解析
Example 2

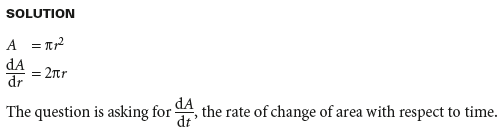


最新發布
? 2025. All Rights Reserved. 滬ICP備2023009024號-1









