- 翰林提供學(xué)術(shù)活動(dòng)、國(guó)際課程、科研項(xiàng)目一站式留學(xué)背景提升服務(wù)!
- 400 888 0080
2021bbo考題深度分析及2022年考點(diǎn)預(yù)測(cè)來了!
春暖花開,又到了每年BBO/USABO考試的季節(jié),大家的辛苦備考也到了最后的沖刺階段,為了幫助各位考生充分利用這最后的一周時(shí)間,我們分析一下2021bbo考題,希望能夠幫助大家理清思路,輕松迎戰(zhàn),考出理想的成績(jī)。
賽事簡(jiǎn)介
英國(guó)中學(xué)生物奧林匹克 (British Biology Olympiad,簡(jiǎn)稱 BBO),該比賽由英國(guó)皇家生物學(xué)(簡(jiǎn)稱 RSB)會(huì)主辦,是英國(guó)中學(xué)歷史最長(zhǎng)、影響最大的理科活動(dòng)之一,每年英國(guó)有近萬名高中生參與。
我們知道BBO和USABO的考試大綱是一樣的,考察的內(nèi)容和所占的分值比例分別為:
Animal anotomy & Physiology(25%)
Cell Biology (20%)
Genetics & Evolution (20%)
Plant Anatomy & Physiology (15%)
Ecology、Ethology & Biosystematics (20%)
下面我們就對(duì)2021年BBO考題在這5大部分里面構(gòu)成的情況和具體考察內(nèi)容進(jìn)行逐一分析:
考題分析
01.Animal anotomy & Physiology
Q2 Part 1-8 ?5分,Q8 Part1-5 10分,共計(jì)15分。占比17%以上
Q2主要考察了免疫系統(tǒng)的humoral response 和cell-mediated response,抗原與抗體的結(jié)合。同時(shí)也考察了學(xué)生對(duì)通路(Pathway)和限速蛋白的理解,相關(guān)概念我們?cè)谡n程里酶的章節(jié)有過詳細(xì)講解。Q8 考察了新冠疫苗開發(fā)的原理以及如何進(jìn)行疫苗有效率的計(jì)算,也是我們課程里面講過的內(nèi)容,先特將疫苗有效率的計(jì)算公式分享給沒有上過課的同學(xué):
02.Cell Biology
Q6 Part?1-8 ?5分,Q7 Part1-7 ?8分,共計(jì)13分。占15%
Q6 以penicillin這個(gè)抗生素為例,考察學(xué)生對(duì)化學(xué)結(jié)構(gòu)決定功能這一規(guī)律的理解以及對(duì)蛋白質(zhì)活性、酶競(jìng)爭(zhēng)性抑制、反饋調(diào)節(jié)、酶催化效率等細(xì)胞生物學(xué)基礎(chǔ)知識(shí)掌握的程度。Q7以病毒為例,考察了學(xué)生對(duì)中心法則的理解以及疫苗的開發(fā)原理。這兩個(gè)考點(diǎn)都是我們?cè)谡n堂上花了大量時(shí)間講解的內(nèi)容,同學(xué)們一定要掌握。
03.Genetics & Evolution?
Q3 Part 1-4 10分,Q5 Part 1-4 ?7分,Q10 Part 1-15 ?14分,共計(jì)21分。占24%
Q3考察了遺傳疾病,遺傳題考查主要集中在非孟德爾遺傳規(guī)律的部分,要充分理解Multiple Alleles, Codominance,Pleiotropy, Epistasis, Polygenic inheritance, Linked gene and crossover, Mitochondrial inheritance, sex-linked 這些各種inheritance pattern 的原理。這一部分的內(nèi)容我們已經(jīng)在課堂上進(jìn)行了充分的練習(xí)和講解,同學(xué)們可以把常染色體顯性遺傳、常染色體隱性遺傳、X染色體連鎖顯性遺傳、X染色體連鎖隱性遺傳和Y染色體連鎖等遺傳的pattern of inheritance 記下來,對(duì)快速解題會(huì)有幫助。
Q5以baobab trees這個(gè)巨大基因組物種為切入點(diǎn),考察了學(xué)生對(duì)基因組、染色體數(shù)目以及減數(shù)分裂的理解。
Q10介紹了基因比對(duì)alignment的原理,考察學(xué)生對(duì)轉(zhuǎn)錄、翻譯等分子生物學(xué)的基礎(chǔ)概念。以及突變和進(jìn)化的分子生物學(xué)基礎(chǔ)。
04.Plant Anatomy & Physiology?
Q4 Part?1-10 ?9分,共計(jì)9分,?占10%
Q4考察的是學(xué)生對(duì)桃子外皮有毛和無毛的理解,這與我們講過的植物葉片的trichomes很類似,同時(shí)也結(jié)合了遺傳學(xué)的內(nèi)容。
05.Ecology、Ethology?& Biosystematics
Q1 Part1-13,Q9 Part1-5 14分,共計(jì)27分。占30%
Q1考察了學(xué)生對(duì)生物群體進(jìn)行統(tǒng)計(jì)的能力,關(guān)于一個(gè)生物群體的Size、Density、Dispersion這些基本概念以及上述指標(biāo)的取樣測(cè)定方法同學(xué)們一定要熟練掌握。Q9以新冠病毒的英國(guó)變種為例,考察了學(xué)生對(duì)于進(jìn)化的推動(dòng)力和進(jìn)化的規(guī)律的理解。
掃碼免費(fèi)領(lǐng)取2021bbo考題及解析,還有名師在線輔導(dǎo)!
站組-1-14.png)
考點(diǎn)預(yù)測(cè)
可以看到,去年的題目有大量關(guān)于人體免疫系統(tǒng)和病毒的內(nèi)容,今年我們?nèi)匀惶幵谛鹿谝咔榇罅餍兄校梭w免疫系統(tǒng)和病毒的內(nèi)容我認(rèn)為任然會(huì)是今年的考試熱點(diǎn)。
同時(shí),20種氨基酸的化學(xué)特性及他們對(duì)蛋白質(zhì)功能和結(jié)構(gòu)的影響,CRISPR/Cas9轉(zhuǎn)基因技術(shù)的原理,植物光合作用C4途徑,神經(jīng)細(xì)胞信號(hào)傳導(dǎo)這些非常重要但是去年沒有考察到的內(nèi)容很有可能出現(xiàn)在今年的考試中。
最后,特將BBO/USABO考試的重要知識(shí)點(diǎn)和重點(diǎn)考察內(nèi)容提供給大家,大家可以按照這個(gè)知識(shí)點(diǎn)列表,對(duì)自己的知識(shí)體系進(jìn)行梳理,希望能夠?qū)Υ蠹矣兴鶐椭?br />
Biochemistry and macromolecules
Cell and cell cycle
Two major types of bonds (ionic bonding and Covalent bonding)
Properties of water
pH is the measure of the acidity and alkalinity
Organic compounds/ macromolecules (Carbohydrates, lipids, protein and nucleic acids)
20 amino acids chemical structure, name and three letter, one letter abbreviation
Four levels of protein structure
Prokaryotes ??VS. ???Eukaryotes
Mitochondrion
chloroplast
Surface vs volume ratio
Cell differentiation
Phases of the cell cycle
Cell cycle regulation
Energy, Metabolism and Enzymes
Cell respiration
Photosynthesis
First and second law of thermodynamics:
Free-energy change
The characteristics of enzyme
Michaelis–Menten Plot of Enzyme Kinetics
Allosteric inhibition of enzyme
Cooperativity of enzyme
Glycolysis
Pyruvate oxidation
Citric acid cycle
Oxidative phosphorylation
Substrate-level phosphorylation
Electron transfer chain
Anaerobic respiration
The light reactions
The Calvin cycle
Plant anatomy and physiology
Angiosperms and Gymnosperms
Ground tissue (Paraenchyma, Collenchyma, Sclerenchyma)
Double fertilization
Stem and root structure of Dicots and Monocots
Primary and Secondary Growth
The formation of lateral root
Simple and compound leaves
Regulation of stoma
Plant hormones
C4 plant anatomy and the C4 pathway
ABC hypothesis
Pressure flow hypothesis
Function of trichomes
The molecular basis of inheritance
genetic engineering
Central dogma
DNA replication
Semiconservative model
Chromatin Packing in a Eukaryotic Chromosome
Transcription
Translation
The initiation of transcription at a eukaryotic promoter.
The genetic code
Bacteria transformation
Polymerase chain reaction?(PCR)
DNA Gel electrophoresis
CRISPR/Cas9 system in E. coli
Genetics and genetic disorder
The human life cycle.
Meiosis
Sexual reproductivity contribute to genetic variation
Mendel’s law of dominance
Law of segregation
The Testcross
The Law of Independent Assortment
Incomplete dominance
Multiple Alleles
Codominance
Pleiotropy
Epistasis
Polygenic inheritance
Linked gene and crossover
Mitochondrial inheritance
Environmental Impact and genotype interaction
Pedigree Analysis
Recessively Inherited Disorders
Dominantly Inherited Disorders
Sex-linked genes
Hardy-Weinberg Equilibrium
Human physiology I
Digestive, Respiratory, Circulatory,
Excretory system
Anatomical Terms
Body planes
Mouth
Esophagus
Stomach
Duodenum
Large intestine
The timing and location of chemical breakdown of macromolecules
Hormones that regulate the digestive system
Medulla in brain control the breath
Hemoglobin
Component of blood
Blood clotting
Structure and function of blood vessels
The human heart:
ECG, electrocardiogram
Ectotherms and Endotherms
Countercurrent heat exchange
Osmoregulation
Kidney
Nephron
Hormone control of the kidneys
Human physiology II
Endocrine, Nervous, Muscle system
Cell communication
Hypothalamus
adrenal gland
antidiuretic hormone (ADH
oxytocin
Posterior pituitary
Anterior pituitary
FSH (Follicle-stimulating hormone)
LH (Luteinizing hormone)
TSH (Thyroid-stimulating hormone)
ACTH (adrenocorticotropic hormone)
Prolactin
MSH: Melanocyte-stimulating hormone
GH: (Growth hormone): stimulate growth of bones
Differences in hormone solubility and structure
Stress and the adrenal gland.
Feedback regulation and coordination with the nervous system
The development of Brain
Reflex Arc
The role of voltage-gated ion channels in the generation of an action potential.
Conduction of an action potential
Schwann cells and the myelin sheath
Synapse
Neurotransmitters
Two mechanisms of terminating neurotransmission.
Eye
Sarcomere
Sarcoplasmic reticulum (SR)
Summation and tetanus
Contraction in a skeletal muscle fiber.
Human physiology III
Immune system and vaccine development
Primary lymphatic organs
Secondary lymphatic organs
Phagocytosis and local inflammatory response
Antigen recognition by T cells
Antigen recognition by B cells and antibodies.
Activation of a B cell in the humoral immune response
The central role of helper T cells in humoral and cell-mediated
Clonal selection
ABO blood type
Vaccine development
Calculation of vaccine efficacy
Evolution, Ecology
Preserving variation in a population
Causes of evolution of a population
Stabilizing selection
Disruptive/diversifying selection
Directional selection
Sexual selection
Artificial selection
Speciation and reproductive isolation
Allopatric and Sympatric speciation
Polyploidy
Habitat isolation
Behavioral isolation
Temporal isolation
Reproductive isolation
Linnaeus’s binomial classification
Phylogenetic trees
Patterns of evolution
divergent, convergent, parallel, coevolution, and adaption radiation evolution
analogous structures
homologous structures
Monophyletic group
Paraphyletic group
Polyphyletic group
Fundamental niche
Realized niche
Properties of population
Symbiosis
Mutualism
Commensalism
Parasitism
Amensalism
Batesian mimicry
Mullerian mimicry
Energy flow and the food chain
距離BBO正式開考還有不到一星期的時(shí)間,已經(jīng)報(bào)名的同學(xué)一定要把握好沖刺的時(shí)間,在上文所提到的重點(diǎn)里找尋更多提分的可能!乘風(fēng)破浪會(huì)有時(shí),直掛云帆濟(jì)滄海,祝大家取得好成績(jī)!
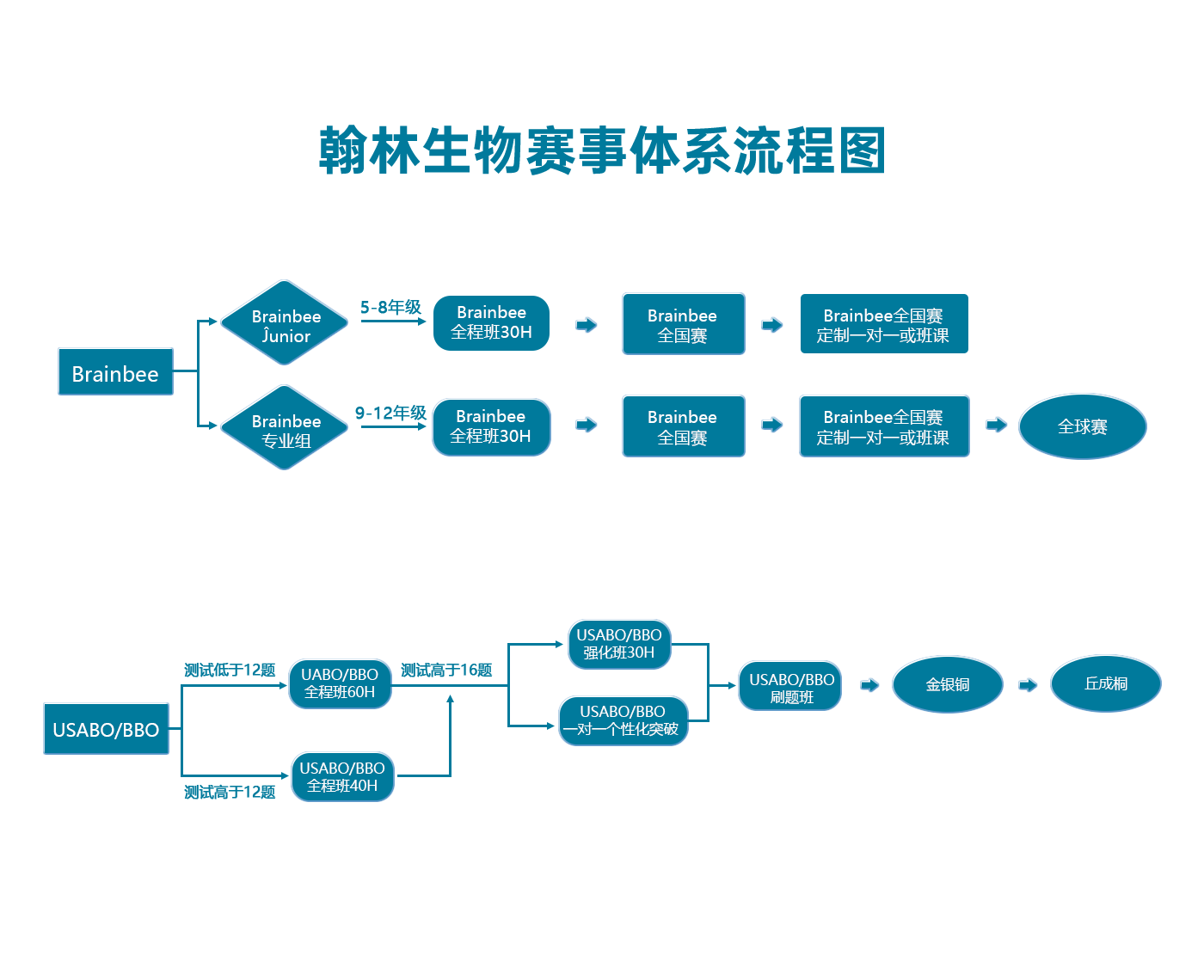
翰林生物學(xué)術(shù)活動(dòng)課程體系流程圖

最新發(fā)布
? 2025. All Rights Reserved. 滬ICP備2023009024號(hào)-1









